Detections Digest #20250602
The issue covers key updates from 10 GitHub repos beetween May 26 and Jun 2, 2025, covering 71 new and 68 modified detection rules.
This week's update highlights the most significant changes to detection rules from 10 of the 40+ monitored GitHub repositories. Between May 26 and Jun 2, 2025, contributors added 71 new rules and updated 68 existing ones.
Stay informed about the latest changes in detection engineering to improve your threat detection coverage and operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
New and updated rules target a wide array of malware and attacker tools. Coverage was added for Katz Stealer, Impacket, Deno execution, various Linux malware (Mobkit, Gafgyt), and numerous Windows threats, including trojans (Cryptbot, Gh0st RAT), ransomware, and Metasploit shellcode. (
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules,elastic/protections-artifacts)Focus on credential access techniques continued with new rules for AS-REP Roasting, registry export of credentials, and disabling LSA Protection. LSASS monitoring was also updated, including detection for suspicious security package loads and refined rules for various LSASS access methods. (
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules,elastic/detection-rules,rabbitstack/fibratus)Detections for LOLBAS abuse, proxy execution, and obfuscation methods were introduced. This includes rules for .NET binaries (dnx, dotnet), Dxcap.exe, obfuscated PowerShell via AmsiScanBuffer, and Linux ld.so proxy execution. (
anvilogic-forge/armory,elastic/protections-artifacts)Email threat detection was improved, targeting various phishing and BEC tactics. New rules identify suspicious Google Drive shares, BEC language, and AppSheet-based phishing, while existing rules for brand impersonation and e-signature fraud were refined. (
sublime-security/sublime-rules,SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules)Microsoft Entra ID and M365 monitoring capabilities were updated. New rules detect user-reported suspicious activity and User Access Administrator elevation in Entra ID, alongside refinements to M365 brute-force detection and service principal credential monitoring. (
elastic/detection-rules)Linux security posture monitoring saw updates with a new rule for ASLR disabling via the
personalitysyscall. Additionally, rules for unexpected setuid binaries and suspicious systemd network activity were refined. (SigmaHQ/sigma,chainguard-dev/osquery-defense-kit,elastic/protections-artifacts)Behavioral detections for Windows defense evasion and persistence were notably updated. This includes identifying event log clearing, hidden registry key creation, process injection, and suspicious modifications to persistence locations or core system modules. (
elastic/protections-artifacts,rabbitstack/fibratus,SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules)
🔔 All new rules mentioned in this issue are available for download as structured STIX2 entities in a free New Detection Rules Feed (over TAXII) at CTIChef.com:
Table Of Contents
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules (+7, ✎2)
elastic/protections-artifacts (+53, ✎38)
SigmaHQ/sigma (+1)
sublime-security/sublime-rules (+2, ✎8)
elastic/detection-rules (+3, ✎2)
Corporate repositories (7)
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules (+7, ✎2)
+ New rules
New rules detect activity related to the Katz Stealer malware, specifically DNS queries to known domains and the loading of associated DLLs. These detections aid in identifying compromised systems. (DNS Query To Katz Stealer Domains, Katz Stealer DLL Loaded)
Added detections for the use of reg.exe to export registry paths linked to third-party credentials, a technique used by credential stealers to extract sensitive information. (Registry Export of Third-Party Credentials, Registry Export of Third-Party Credentials)
A new rule identifies file creation events using filename patterns associated with the Impacket framework, which is often used in post-exploitation activity. (HackTool - Impacket File Indicators)
A new rule identifies Deno writing files from direct HTTP(s) calls to the appdata folder or including malicious DLLs, which can point to the execution of remote, malicious files. (Suspicious Deno File Written from Remote Source)
A new rule identifies suspicious Kerberos TGT requests with pre-authentication disabled and RC4-HMAC encryption, potentially indicating an AS-REP Roasting attack. (Potential AS-REP Roasting via Kerberos TGT Requests)
✎ Modified rules
Rules were updated to expand detection of command-line access to 3rd party registry keys known to store credentials. Updates add registry keys and improve filtering to reduce false positives. (Enumeration for 3rd Party Creds From CLI, Enumeration for 3rd Party Creds From CLI)
elastic/protections-artifacts (+53, ✎38)
+ New rules
New YARA rules added for Linux malware detection. These rules identify the Mobkit rootkit, Autocolor trojan, Xmrminer cryptominer, and Gafgyt trojan by scanning for specific strings and byte patterns in files and memory on x86 and arm64 architectures. (Linux_Rootkit_Mobkit_335e48bc, Linux_Trojan_Autocolor_18203450, Linux_Cryptominer_Xmrminer_02d19c01, Linux_Trojan_Gafgyt_09c3070e)
Multiple new YARA rules now detect a range of Windows-based malware. This includes hacktools (Nimhawk), ransomware (Vgod), trojans (Cryptbot, ACRStealer, KoiLoader, LegionLoader, Gh0st RAT, Winos, Latrodectus, WarmCookie). Detections are based on unique strings, byte sequences, and file names associated with each malware family, targeting files and memory. (Windows_Hacktool_Nimhawk_cdcc3540, Windows_Ransomware_Vgod_86a877fd, Windows_Trojan_Cryptbot_489a6562, Windows_Trojan_ACRStealer_f9728d76, Windows_Trojan_KoiLoader_1131bc57, Windows_Trojan_LegionLoader_9699226a, Windows_Trojan_Gh0st_9e4bb0ce, Windows_Trojan_Winos_464b8a2e, Windows_Trojan_Latrodectus_841ff697, Windows_Trojan_WarmCookie_344e4d3f)
New YARA rules have been implemented to detect the EmpirGo and Goffloader trojans. These rules focus on detecting specific strings within the malware's code, which aids in identifying infected systems. (Multi_Trojan_EmpirGo_38a23b2c, Multi_Trojan_Goffloader_d1f4201e)
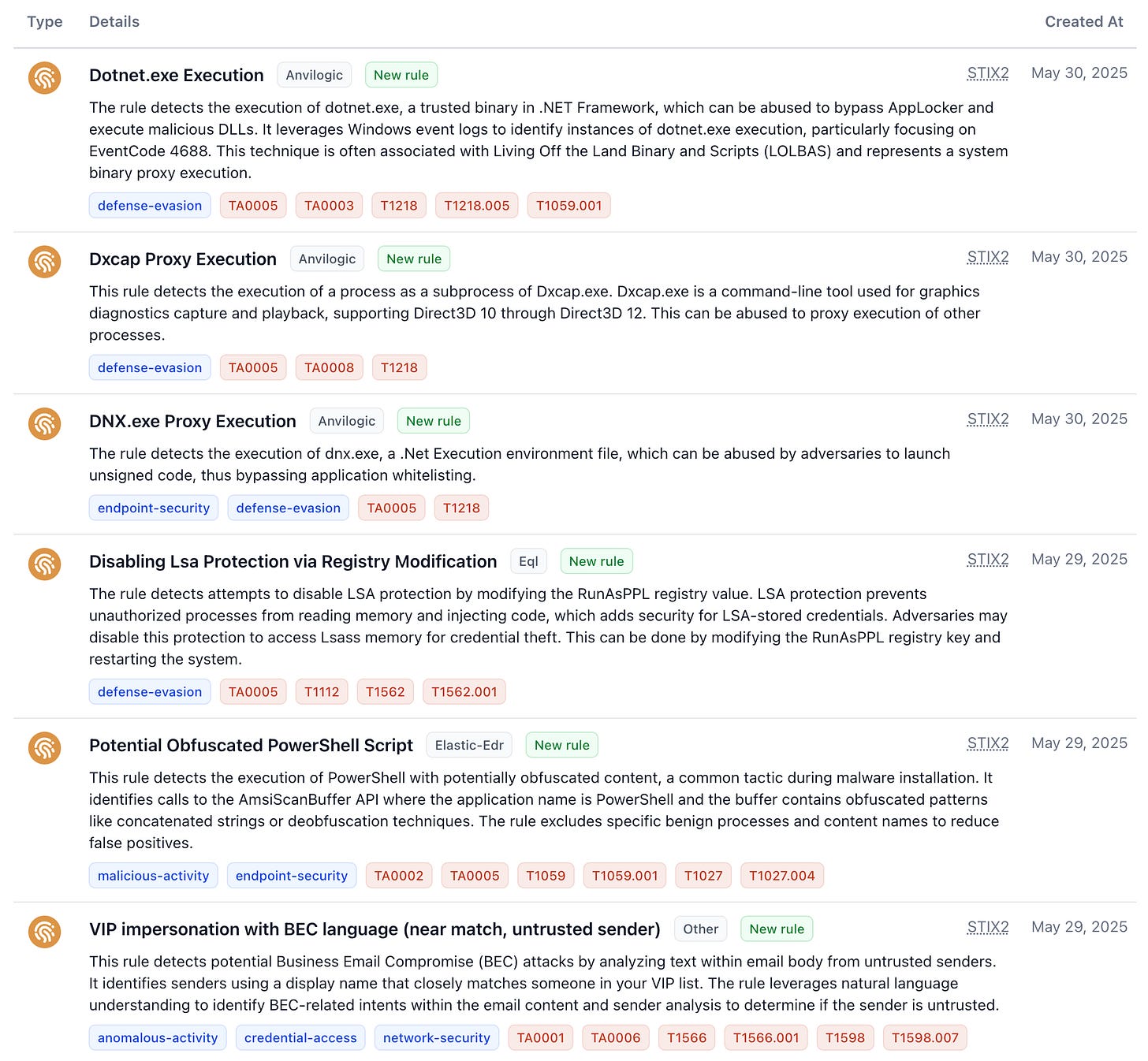
A new Elastic EDR rule detects potentially obfuscated PowerShell execution, which is a common malware installation tactic. The rule focuses on calls to the AmsiScanBuffer API with obfuscated content, while excluding benign processes to lower false positives. (Potential Obfuscated PowerShell Script)
✎ Modified rules
Detection added for Linux.Trojan.Gafgyt by identifying binary code patterns on x86 architectures in file and memory scans. (Linux_Trojan_Gafgyt_09c3070e)
Detection implemented for Windows.Trojan.Cryptbot based on file paths and command-line arguments, specifically targeting temporary file removal and access to password and cryptocurrency information. (Windows_Trojan_Cryptbot_489a6562)
Multiple rules detect Windows Generic Threats by identifying specific byte sequences commonly associated with malicious Windows executables in file and memory scans. (Windows_Generic_Threat_005fd471)
Detection added for Windows-based threats, focusing on specific variants of the Gh0st RAT based on strings and the WarmCookie Trojan based on memory and file scans. (Windows_Trojan_Gh0st_9e4bb0ce, Windows_Trojan_WarmCookie_344e4d3f)
Several rules detect the API address lookup function used by Metasploit shellcode and kernel to user shellcode, which may also be used by tools like Beacon, aiding in identifying potential exploitation attempts. (Windows_Trojan_Metasploit_24338919)
Multiple rule updates improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives across various attack techniques. This includes adding exclusions for legitimate processes and files, filtering network connections, refining regex patterns, and addressing memory protection changes in core modules. Specific areas of improvement are seen in discovery command detection, outbound network connections to .oast domains, dynamic linker usage, process self-deletion, persistence mechanisms, macOS Finder cache modifications, base64 encoded strings in AppleScript, unusual API calls, file name masquerading, memory API access, persistence locations modification and network module loading. (Discovery Result Written to a Suspicious File via Discovery Process, Network Connection to Oast Domain via Package Service or Script, System Binary Proxy Execution via ld.so, Unsigned or Untrusted Process Execution and Immediate Self-Deletion, Systemd Execution Followed by Network Connection, Suspicious Finder Cache File Modification, Base64 Encoded String Execution via Osascript, API Call via Jump ROP Gadget, Potential Known TCP Port Traffic Tunneling, Library Loaded via a CallBack Function, Execution of a Windows Script Downloaded via a LOLBIN, Evasion via File Name Masquerading, Suspicious API call via a Windows Installer Module, Suspicious Windows Core Module Change, Suspicious API Call from a PowerShell Script, Windows API Call via Indirect Random Syscall, Network Connection via Startup Item, Lateral Execution via DCOM Office Application, Execution from Suspicious Stack Trailing Bytes, Startup Persistence via Windows Script Interpreter, NetworkCleartext Logon by a Suspicious Process, Network Module Loaded from Suspicious Unbacked Memory)
📰 Cyber OSINT Overview consolidates updates from over 80 sources, including government organizations, cybersecurity vendors, threat intelligence teams, security research labs, and blogs from cybersecurity communities and professionals, and delivers a weekly summary to your inbox.
chainguard-dev/osquery-defense-kit (✎1)
✎ Modified rules
The 'Unexpected setuid binaries' rule now has better coverage due to added paths to its exclusion list. This prevents false positives related to common binaries, while still identifying potential privilege escalation vectors. (1-unexpected-setuid-binaries.sql)
SigmaHQ/sigma (+1)
+ New rules
A new rule identifies the disabling of Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) in Linux by monitoring the personality syscall with the ADDR_NO_RANDOMIZE flag. Attackers use this to make memory corruption attacks more reliable. (Disable ASLR Via Personality Syscall - Linux)
sublime-security/sublime-rules (+2, ✎8)
+ New rules
New rules provide detection for suspicious Google Drive shares and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks. The 'Detects suspicious Google Drive Shares containing inappropriate content' rule identifies reports from non-organizational domains with explicit keywords. The BEC rule, 'This rule detects potential Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks by analyzing text within email body from untrusted senders', detects senders impersonating VIPs and analyzes email content for BEC intent. (Spam: Sexually Explicit Google Drive Share, VIP impersonation with BEC language (near match, untrusted sender))
✎ Modified rules
Several rules addressing brand impersonation in emails were updated. These include improved detection for SendGrid, Google Drive, Dropbox, and Sharepoint impersonation attempts. The rules use sender/content analysis, machine learning, and computer vision to identify phishing emails and credential theft attempts, with added checks to reduce false positives in reply emails. (Brand Impersonation: SendGrid, Brand impersonation: Google Drive fake file share, Brand impersonation: Dropbox, Brand impersonation: Sharepoint, Brand impersonation: Sharepoint fake file share)
The rule for detecting e-signature phishing was updated to include a new condition that checks for emails containing a single hyperlinked image and short text. This improves detection of sophisticated phishing attempts using visual cues. (Credential Phishing: Suspicious E-sign Agreement Document Notification)
The rule for detecting tax preparation assistance requests from unknown senders was updated to include a check for short subject lines. This improves coverage for potential BEC and fraud attempts. (Fake request for tax preparation)
The rule for detecting suspicious Google Groups invitations was updated to include the lust keyword for sexually explicit content. This update expands coverage for detecting spam related to explicit content within Google Groups. (Spam: Sexually Explicit Google Group Invitation)
elastic/detection-rules (+3, ✎2)
+ New rules
The 'Suspicious Activity Reported by User' rule detects potential account compromise in Microsoft Entra ID by monitoring user-reported suspicious activity related to their accounts during the authentication process. (Microsoft Entra ID User Reported Suspicious Activity)
The 'User Access Administrator Elevation' rule detects when a user elevates their access to User Access Administrator for their Azure resources, potentially leading to privilege escalation and unauthorized resource access. This rule only triggers if the user principal name has not performed this action in the last 14 days. (Microsoft Entra ID Elevated Access to User Access Administrator)
The 'Disable LSA Protection' rule identifies attempts to disable LSA protection via registry modifications, a technique adversaries may use to access Lsass memory for credential theft. (Disabling Lsa Protection via Registry Modification)
✎ Modified rules
The 'New Service Principal Credentials Added' rule was updated to modify the index used to search events and adds a reference URL regarding cyber threat activity targeting Commvault's SaaS cloud application Metallic. (Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal Credentials Added by Rare User)
The 'Microsoft 365 Brute-Force Attack' rule was updated to broaden the analysis scope by adjusting the time frame and introducing a time window. This allows for a longer period to be analyzed. (Potential Microsoft 365 User Account Brute Force)
anvilogic-forge/armory (+3)
+ New rules
Two rules identify abuse of .NET binaries (dnx.exe and dotnet.exe) to run unsigned code or bypass application whitelisting. The rules look for execution of these binaries, a technique known as Living Off the Land Binary and Scripts (LOLBAS). (DNX.exe Proxy Execution, Dotnet.exe Execution)
A new rule detects the proxy execution of processes using Dxcap.exe, a command-line tool for graphics diagnostics. This helps uncover potential abuse of Dxcap.exe for malicious purposes. (Dxcap Proxy Execution)
Personal repositories (3)
SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules (+1, ✎1)
+ New rules
A new rule identifies phishing attempts using AppSheet.com to mimic Meta (Facebook), inspecting email subject, sender address, and display name for relevant keywords. (AppSheet.com abused to send Phish)
✎ Modified rules
Detection of DefendNot activity is improved. The 'DefendNot ctx.bin File Creation' rule now monitors for FileCreated events involving the creation of ctx.bin files on devices in passive EDR mode, rather than registry key modifications, using data from Microsoft Defender XDR. (defendnot detection)
alexverboon/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules (✎2)
✎ Modified rules
The 'McasShadowItReporting' queries for shadow discovery information are updated to filter telemetry based on the stream name 'Defender-managed endpoints', instead of the deprecated 'Win10 Endpoint Users'. This change aims to maintain accurate reporting by using the correct data stream. (MCAS Shadown Reporting details by Application, MCAS Shadown Reporting details by Application)
rabbitstack/fibratus (+1, ✎14)
+ New rules
A new rule detects the loading of a suspicious security package DLL into lsass.exe. The rule monitors lsass.exe for module loads matching sspisrv.dll and unsigned or untrusted modules, which could indicate credential dumping. (Suspicious security package DLL loaded)
✎ Modified rules
Several rules related to LSASS access were updated. These rules identify suspicious or unauthorized access to LSASS, memory dumps, or remote thread creation, often indicators of credential theft attempts. Updates standardize event property access to evt.arg[exe] and raise the minimum engine version. (LSASS access from unsigned executable, LSASS handle leak via Seclogon, LSASS memory dumping via legitimate or offensive tools, LSASS memory dump via MiniDumpWriteDump, Remote thread creation into LSASS)
The 'Clear Windows Event Logs' rule was updated. This rule identifies attempts to clear event logs, a common tactic used by adversaries to evade detection. The update modifies the event property accessed (kevt.pid to evt.pid) and raises the minimum engine version. (Clear Eventlog)
The 'Hidden Registry Key Creation' rule was updated. This rule identifies the creation of hidden registry keys, a technique used by adversaries to conceal malicious payloads for persistence. The update changes the event property accessed (kevt.pid to evt.pid) and increases the minimum engine version. (Hidden registry key creation)
Multiple rules that identify suspicious activity were updated. These rules cover NTFS transaction abuse, shellcode execution, process injection, RX memory mapping, object symbolic link creation, and persistence via Run keys. All rules now use evt.pid instead of kevt.pid and require a minimum engine version of 3.0.0. (Image load via NTFS transaction, Potential shellcode execution via ETW logger thread, Potential process injection via tainted memory section, Suspicious DLL loaded via memory section mapping, Suspicious object symbolic link creation, Script interpreter host or untrusted process persistence)
The 'Unsigned DLL Loaded by Print Spooler' rule was updated to exclude the spoolsv.exe process name from triggering the alert. The rule identifies the loading of unsigned DLLs by the print spool service, a common technique for persistence. (Suspicious port monitor loaded)
Feedback
Your input helps us improve! If you spot any issues, mistakes, or omissions in this digest issue, or have suggestions for new data sources to include, we'd love to hear from you. Contact us at team@rulecheck.io - we value your feedback and are committed to improving this resource for the detection engineering community.
Disclaimer
The summaries in this brief are generated autonomously by the OpenAI LLM model based on the provided system and user prompts. While every effort is made to consolidate accurate and relevant insights, the model may occasionally misinterpret, misrepresent, or hallucinate information. Readers are strongly advised to verify all key points by consulting the sources linked in the brief for complete context and accuracy.
Powered by
This digest is built with BlackStork.
Looking for a customized version of this newsletter? We'd be happy to help — contact us.