Detections Digest #20250526
The issue highlights key changes from 9 GitHub repositories for the week of May 5 to May 12, 2025 and introduces new Detection Feeds 🚀
This week's update highlights the most significant changes to detection rules from 9 of the 40+ monitored GitHub repositories. Between May 19 and May 26, 2025, contributors added 85 new rules and updated 56 existing ones.
And we have some exciting news! 🚀 Read the update below!
Stay informed on the latest changes in detection engineering to improve your threat detection coverage and operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Improved cloud threat detection for AWS, Azure, and Microsoft 365. New rules target sophisticated AWS API abuse (e.g., malicious Lambda deployment, disabling monitoring services, federation token abuse), Microsoft 365 credential attacks (brute-force, password spraying), unauthorized Microsoft Graph API access, and novel Azure C2/reconnaissance techniques like EntraFalcon and C2 over Azure Blob metadata. (
anvilogic-forge/armory,elastic/detection-rules,SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules)Focus on advanced endpoint evasion and stealthy execution. Detection capabilities were significantly boosted for stealthy PowerShell usage (renamed binaries, FakeCAPTCHA clipboard hijacking, headless ConHost execution) and data exfiltration via Chromium's headless debugging mode. Many existing rules for WMI, PowerShell/WinRM remoting, and delayed execution were also refined for improved accuracy and broader coverage. (
splunk/security_content,Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules,SigmaHQ/sigma,elastic/detection-rules)Major expansion and refinement of email-borne threat detection. A substantial number of new rules address open redirect vulnerabilities across various legitimate services, with many existing detections now leveraging DMARC for more accurate trusted sender validation. New detections also cover service abuse (e.g., unsolicited Zoom Docs), impersonation (e.g., USDA, Sharepoint), and social engineering tactics like mismatched free email provider reply-to addresses. (
sublime-security/sublime-rules)Increased coverage for specific malware, vulnerabilities, and reconnaissance Tools. New detections were added for threats such as Lumma Stealer, EddieStealer (YARA), numerous generic malicious Windows certificates (YARA), and the exploitation of vulnerabilities, including Veeam CVE-2023-27532 and emerging CVEs (Chrome zero-day, Outlook OOB, and glibc). Reconnaissance tool detection was also improved for Adfind (including renamed versions), CrackMapExec, and Atera RMM. (
splunk/security_content,elastic/protections-artifacts,SigmaHQ/sigma,Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules,SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules)Strengthened monitoring for Active Directory and identity security. New rules improve visibility into suspicious Active Directory changes, including object OU moves, 'Password Not Required' flag modifications, GPO manipulations, and unusual outbound Kerberos traffic. (
alexverboon/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules,SigmaHQ/sigma)Improved detection of defense evasion and blinding techniques. Attackers' attempts to operate undetected are now better covered with new rules for disabling IIS logging (ETW/HTTP), detecting antivirus software in passive mode (Microsoft Defender), identifying deletion of Kubernetes events, and flagging attempts to disable AWS monitoring services. (
SigmaHQ/sigma,SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules,anvilogic-forge/armory)Proactive threat hunting via OSINT IOC Correlation. New rules have been added that cross-reference endpoint, email, and network activity against weekly external OSINT feeds of known malicious indicators, such as file hashes, URLs, domains, and IP addresses. (
SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules)
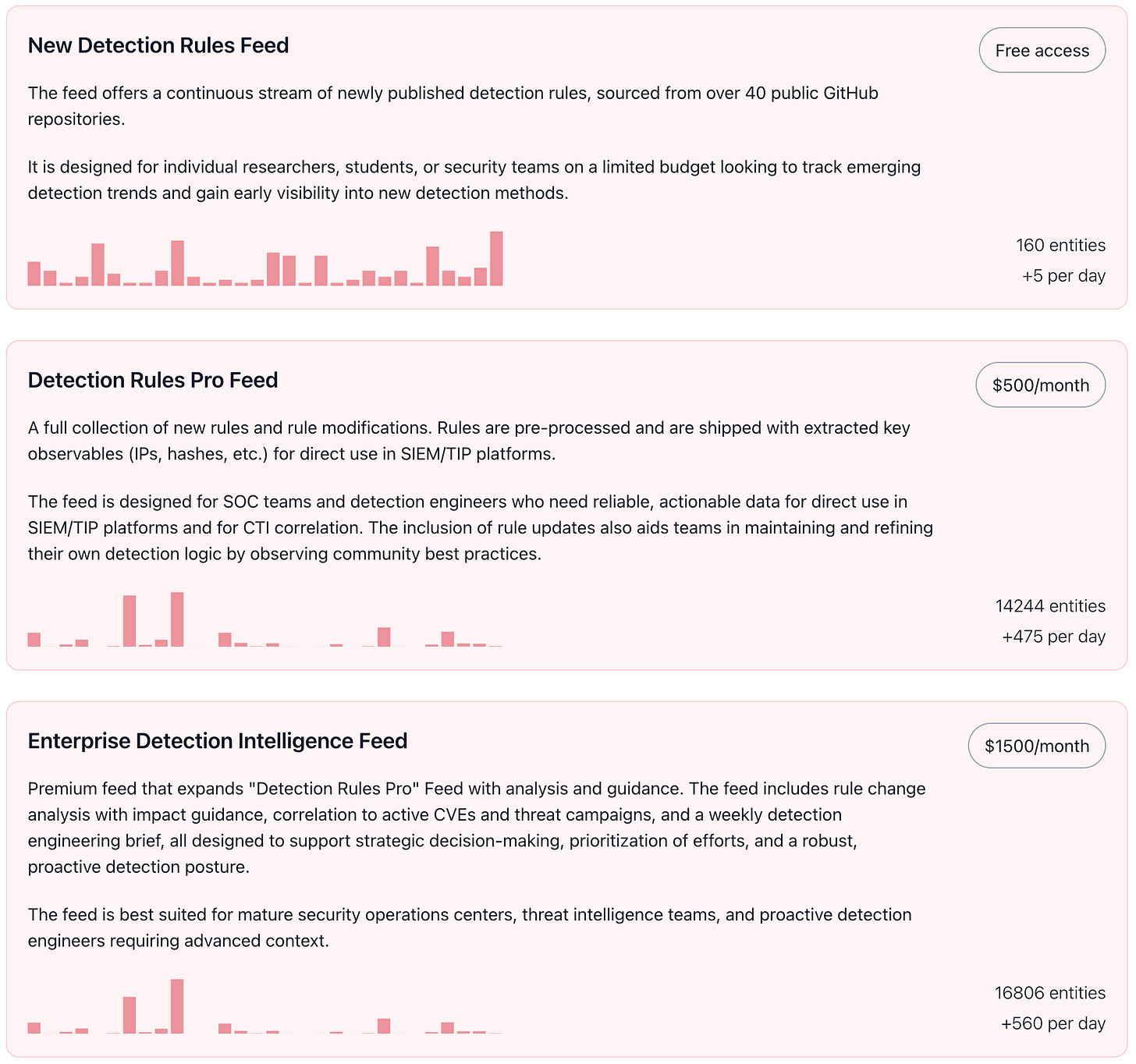
🤖 Turn Insights into Active Defense: Introducing Our New Detection Feeds! 🚀
Enjoying this weekly digest?
Now you can get the rule updates delivered directly to your security tools in a ready-to-use structured format with our new Threat Detection CTI Feeds.
We do the heavy lifting for you:
Continuous monitoring: We track over 40+ detection rule repositories on GitHub for new rules and updates to existing ones.
Actionable details extracted: We don't just give you raw rules. We extract the key details (such as suspicious IP addresses, file hashes, domain names, and other observables) and ship them with the rules, making it easy to connect the detections to other threat warnings or intelligence you're already tracking.
Understand what changed: We provide insights into the changes for updated rules, helping you quickly assess the impact and relevance to your environment.
Ready for your tools: The feeds are STIX2 intel feeds, and easily integrate with your SIEM, SOAR, and Threat Intelligence Platforms, allowing you to ship detections directly to your defenses.
Reduce manual effort in sourcing and processing detection rules. Get these feeds to speed up your detection content pipeline and free up analyst resources for more high-value tasks.
Table Of Contents
elastic/detection-rules (+2, ✎7)
splunk/security_content (+8, ✎4)
SigmaHQ/sigma (+8, ✎2)
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules (+5, ✎5)
sublime-security/sublime-rules (+12, ✎38)
Corporate repositories (7)
anvilogic-forge/armory (+3)
+ New rules
New rules target suspicious AWS CloudTrail API calls. The 'DisableAWSServiceAccess' rule spots attempts to disable service-linked roles, which could disrupt monitoring. 'GetFederationToken' detects possible initial access, privilege escalation, or persistence via temporary AWS credentials. 'AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole' identifies suspicious attachments of the Lambda execution role policy, potentially revealing preparations for malicious Lambda function deployments. (AWS DisableAWSServiceAccess, AWS GetFederationToken, AWS AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole Attached)
elastic/detection-rules (+2, ✎7)
+ New rules
New rules detect Microsoft 365 brute-force and password spraying attacks. The 'M365 Account Lockout Burst' rule identifies high volumes of IdsLocked login errors, while the 'M365 Brute-Force Authentication' rule spots failed sign-in patterns indicative of password spraying or credential stuffing. (Multiple Microsoft 365 User Account Lockouts in Short Time Window, Potential Microsoft 365 User Account Brute Force)
✎ Modified rules
The New Terms rule focuses on detecting unauthorized access to Microsoft Graph API by looking at the first request from a client application for a specific tenant and user, which helps identify compromised accounts using the Graph API. (Microsoft Graph First Occurrence of Client Request)
Detection of first-time scheduled task modifications by user accounts is updated to utilize a kuery-based query for improved efficiency, focusing on event code 4702 and excluding system accounts. (Unusual Scheduled Task Update)
The rule detecting modifications to run keys or startup keys in the registry was updated to incorporate additional process names and registry data strings to improve the detection of persistence mechanisms. (Startup or Run Key Registry Modification)
Rules detecting remote command execution via WMI, PowerShell remoting, and WinRM have been updated. The WMI rule has improved argument detection for lateral movement. PowerShell and WinRM rules broaden scope by removing network protocol conditions. The WMI processes rule has an increased maxspan and a specific destination port filter. (Suspicious Cmd Execution via WMI, WMI Incoming Lateral Movement, Incoming Execution via PowerShell Remoting, Incoming Execution via WinRM Remote Shell)
splunk/security_content (+8, ✎4)
+ New rules
Rules added to detect Lumma Stealer activity using Cisco Secure Firewall Intrusion Events. These rules identify download attempts, general activity, and outbound connections associated with the stealer by monitoring Snort signature IDs. (Cisco Secure Firewall - Lumma Stealer Download Attempt, Cisco Secure Firewall - Lumma Stealer Activity, Cisco Secure Firewall - Lumma Stealer Outbound Connection Attempt)
New rules use Cisco Secure Firewall Intrusion Events to detect threat activity by correlating Snort signatures and identifying high-severity intrusion events based on Snort rule classifications. These rules use a lookup table to map Snort IDs to threat actors, flagging potential coordinated actions. (Cisco Secure Firewall - Intrusion Events by Threat Activity, Cisco Secure Firewall - High Priority Intrusion Classification)
Rules added for detecting renamed PowerShell executables used for evasion and FakeCAPTCHA clipboard hijacking campaigns. The PowerShell rule detects executions where the process name differs from defaults. The FakeCAPTCHA rule identifies PowerShell execution with hidden windows and strings related to fake CAPTCHA verification used in clipboard hijacking. (Windows Renamed Powershell Execution, Windows PowerShell FakeCAPTCHA Clipboard Execution)
A rule was added to detect exploitation of CVE-2023-27532 in Veeam Backup & Replication using Cisco Secure Firewall Intrusion Events. The rule spots a credential dump attempt followed by xp_cmdshell invocation, suggesting potential remote command execution. (Cisco Secure Firewall - Veeam CVE-2023-27532 Exploitation Activity)
✎ Modified rules
The WMIC process enumeration rule was updated to focus on command-line executions, improving specificity when detecting adversaries gathering process information. (Windows Process Commandline Discovery)
The 'ping sleep batch commands' rule now includes '>' and '&' symbols in its detection logic, broadening coverage for delayed code execution attempts. (Ping Sleep Batch Command)
The msiexec.exe /y switch detection was updated to modify the process IN clause improving the identification of msiexec.exe processes executing with the /y switch parameter. (Windows MSIExec DLLRegisterServer)
The 'Schtasks scheduling job on remote system' detection was updated to adjust the process command-line search to correctly identify tasks scheduled on remote systems. (Schtasks scheduling job on remote system)
SigmaHQ/sigma (+8, ✎2)
+ New rules
Two new rules identify modifications to IIS server configuration to disable ETW logging/processing and HTTP logging, which could indicate an attempt to evade detection. (ETW Logging/Processing Option Disabled On IIS Server, HTTP Logging Disabled On IIS Server)
The rule 'Chromium Headless Debugging User Profile' identifies chromium based browsers running in headless and debugging mode and pointing to a user profile, which may indicate data theft or remote control. (Potential Data Stealing Via Chromium Headless Debugging)
A new rule detects the execution of Adfind.exe, a utility often employed for reconnaissance within Active Directory environments. (PUA - AdFind.EXE Execution)
The rule 'Outbound Kerberos Traffic' detects unusual outbound network traffic on the default Kerberos port, signaling possible lateral movement or initial Privilege Escalation through delegation. (Uncommon Outbound Kerberos Connection - Security)
Three new rules provide visibility into Kubernetes event deletion, Atera RMM agent installation, and system bugcheck errors. The 'Kubernetes Event Deletion' rule detects when events are deleted in Kubernetes. The rule 'Atera RMM Installation' detects installs of the Atera agent used by Conti operators. The rule 'Windows BugCheck Error' monitors system crashes. (Kubernetes Events Deleted, Atera Agent Installation, Crash Dump Created By Operating System)
✎ Modified rules
Detection coverage for post-compromise reconnaissance activity is improved. The 'findstr' rule now has additional MITRE ATT T CK technique and tactic IDs for better alignment. Also, detection of renamed Adfind.exe binaries now uses additional IMPHASH values. (Insensitive Subfolder Search Via Findstr.EXE, Renamed AdFind Execution)
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules (+5, ✎5)
+ New rules
New rules added to detect execution of Adfind.exe for Active Directory reconnaissance. These rules expand visibility into adversary actions within Active Directory environments. (PUA - AdFind.EXE Execution, PUA - AdFind.EXE Execution)
A new rule detects "BugCheck" errors, capturing details like bugcheck code, dump file path, and report ID. This adds capability to analyze system crashes and identify potential underlying issues. (Crash Dump Created By Operating System)
A new rule identifies file creation events associated with CrackMapExec, aiding in the detection of lateral movement and post-exploitation activity. (HackTool - CrackMapExec File Indicators)
A new rule detects PowerShell commands executed from a headless ConHost window (using the "--headless" flag), revealing attempts to hide PowerShell execution from users. (Powershell Executed From Headless ConHost Process)
✎ Modified rules
Coverage for detecting renamed Adfind.exe, a tool used for domain trust discovery, was improved by including additional IMPHASH values. (Renamed AdFind Execution, Renamed AdFind Execution)
Rules detecting findstr usage and Windows Defender setting modifications now have added MITRE ATT ACK TIDs for improved mapping to the ATT ACK framework. (Insensitive Subfolder Search Via Findstr.EXE, Potential Windows Defender Tampering Via Wmic.EXE)
The 'Potential COM object hijacking via modification of default system CLSID' rule has been updated with a new CLSID and a reference URL, which improves coverage and context for COM object hijacking detection. (COM Object Hijacking Via Modification Of Default System CLSID Default Value)
sublime-security/sublime-rules (+12, ✎38)
+ New rules
Several new rules identify email-borne threats exploiting open redirect vulnerabilities on various domains (Keap, documentmailbox.com, Artisteer, Doubleclick.net, easycamp.com, learningapps.org, fenc.com, PIRL San Diego, and ringaraja.net). These rules check inbound emails for links containing specific paths and query parameters indicative of open redirects, while often excluding trusted senders unless DMARC checks fail. (Link: Direct Link to keap.app contact-us page, Open Redirect: documentmailbox.com, Open redirect: Artisteer, Open redirect: Doubleclick.net, Open Redirect: easycamp.com, Open Redirect: LearningApps, Open Redirect: fenc.com, Open Redirect: PIRL San Diego, Open Redirect: ringaraja.net)
A new rule detects messages from Zoom Docs originating from newly observed email addresses. The email address is extracted from the message body. (Service Abuse: Zoom Docs From an Unsolicited Sender Address)
A new rule detects messages claiming to be from the USDA that contain bid invitations with macro-enabled attachments or PDFs. The rule validates USDA-related content through OCR and natural language analysis. (Attachment: USDA Bid Invitation Impersonation)
A new rule detects social engineering tactics where a sender using a free email provider includes a reply-to address from a different free email provider. (Free Email Provider Sender with Mismatched Provider Reply-To)
✎ Modified rules
Multiple rules addressing open redirect abuse were updated. These rules detect phishing attempts by negating highly trusted sender domains only when DMARC authentication fails, replacing previous logic based on sender profiles. This shift improves accuracy when identifying malicious usage of various open redirect services. (Open Redirect: events.csiro.au, Open redirect: Dell, Open redirect: City of Calgary, Open Redirect: bestdeals.today, Open Redirect: Club-OS, Open Redirect: chkc.com.hk, Open Redirect: artkaderne, Open redirect: people.anuneo.com, Open Redirect: g7.fr, Open Redirect: isadatalab.com, Open Redirect: ExacTag, Open redirect: marketing.edinburghairport.com, Open Redirect: eodcnetworkdirect.com, Open Redirect: LinkedIn Redirect, Open redirect: Nested Doubleclick.net, Open Redirect: magneticmarketing.com, Open redirect: Newegg, Open Redirect: nowlifestyle.com, Open redirect: giving.lluh.org, Open Redirect: Medium, Open Redirect: phoenixartstudio.net, Open redirect: next2.io, Open redirect: Ticketmaster, Open Redirect: pmifunds.com, Open Redirect: TikTok, Open Redirect: PremierBet, Open redirect: slubnaglowie.pl, Open Redirect: stats.lib.pdx.edu, Open Redirect: storematch.jp, Open redirect: Signature Travel Network, Open Redirect: xfinity.com, Open Redirect: ust.hk, Open Redirect: Xfinity CMP Redirection to Google AMP)
Rules for e-signature phishing and Sharepoint impersonation were updated. Detection for e-signature attempts is improved by checking for suspicious content in link display text. The Sharepoint rule now checks for Excel, SharePoint, PowerPoint, and OneNote in the sender display name and subject and identifies spoofed emails from internal domains that fail SPF or DMARC. (Credential Phishing: Suspicious E-sign Agreement Document Notification, Brand impersonation: Sharepoint fake file share)
The 'Recon messages' rule now includes an additional condition to check if the body length without a disclaimer is shorter than 50 characters. This refines the detection of deliverability testing emails. (Reconnaissance: Large unknown recipient list)
The 'Detect fraudulent invoices/receipts' rule now uses beta.html_xpath for parsing HTML email bodies, focusing on tables after the first image and before a footer. The rule now filters out non-actor-controlled details and has improved logic to detect fraud keywords. (PayPal Invoice Abuse)
The rule detecting redirects via typedrawers.com now has removed a condition related to sender reputation and solicited status. This change may address false negatives in the original detection logic. (Open redirect: typedrawers.com)
elastic/protections-artifacts (+29)
+ New rules
New YARA rules identify Windows Generic Malicious Certificates via byte pattern matching in files. These rules offer improved capability to detect potentially compromised certificates on Windows systems. (Windows_Generic_MalCert_ec4381c9, Windows_Generic_MalCert_024569d4, Windows_Generic_MalCert_871164db, Windows_Generic_MalCert_101ac60e, Windows_Generic_MalCert_abeefc63, Windows_Generic_MalCert_234b63fb, Windows_Generic_MalCert_ab8661e1, Windows_Generic_MalCert_6926a408, Windows_Generic_MalCert_ff00d21d, Windows_Generic_MalCert_f20eba4e, Windows_Generic_MalCert_30719a7d, Windows_Generic_MalCert_ec2b87b1, Windows_Generic_MalCert_c9e89da2, Windows_Generic_MalCert_326bc791, Windows_Generic_MalCert_e822d2d7, Windows_Generic_MalCert_cf230984, Windows_Generic_MalCert_082de32b, Windows_Generic_MalCert_a47f5902, Windows_Generic_MalCert_a318116e, Windows_Generic_MalCert_d743cb47, Windows_Generic_MalCert_21c05181, Windows_Generic_MalCert_276c83b7, Windows_Generic_MalCert_2a46688e, Windows_Generic_MalCert_eb360bb1, Windows_Generic_MalCert_5f0656b2, Windows_Generic_MalCert_59ff12f8, Windows_Generic_MalCert_c3d5b526, Windows_Generic_MalCert_11e18261)
A new YARA rule identifies the EddieStealer infostealer. This rule uses specific byte sequences to detect the malware in file and memory scans. (Windows_Infostealer_EddieStealer_12a21c75)
Personal repositories (2)
alexverboon/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules (+8)
+ New rules
New rules monitor Active Directory for changes to computer object OS names, account 'Password Not Required' settings, and user/device object OU moves. These detections use Microsoft Defender XDR IdentityDirectoryEvents and DeviceEvents tables to identify changes, providing visibility into potential privilege escalation or lateral movement. (AD-ComputerObjectOSNameChanged, Active Directory - Account Password Not Required changed, Active Directory - User or Device object OU moves)
New rules identify Group Policy Object (GPO) activity within Active Directory, specifically creation, modification and display name changes. These rules use the IdentityDirectoryEvents and DeviceEvents tables, with detections focused on the 'Group Policy was created', 'Group Policy settings were changed', and 'Group Policy Display Name changed' action types. This allows for observation of potential policy manipulation. (Group Policy was created, Group Policy settings were changed, DirectoryServiceObjectCreated, Group Policy Display Name changed)
SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules (+10)
+ New rules
New rules detect threats by correlating endpoint, email, and network activity with external OSINT IOC feeds, ingested as CSV files from GitHub. These rules cross-reference indicators such as file hashes (SHA256, SHA1, MD5), domains, URLs, and IP addresses against various data sources within Defender XDR. (DefenderXDR Weekly OSINT Indicators Scan 05052025, DefenderXDR Weekly OSINT Indicators Scan 12052025, DefenderXDR Weekly OSINT Indicators Scan 19052025)
Several new rules detect exploitation attempts targeting specific CVEs. These rules focus on identifying vulnerable systems and suspicious behaviors associated with CVE-2025-4664 (Chrome zero-day), CVE-2025-32705 (outlook.exe out-of-bounds read), and CVE-2025-4802 (glibc vulnerability), using data related to process execution, file creation, and memory access. (Global Admin Entra Cookie with Chrome ZeroDay, CVE-2025-32705 Out-of-bounds Read Detection, glibc critical vulnerability (CVSS 9.8))
A new rule identifies the usage of EntraFalcon, a tool for enumerating Entra ID objects, by monitoring sign-in events tied to application IDs and resource identities known to be used by this tool. (EntraFalcon Detection)
A new rule spots potential C2 communications where devices interact with Azure Blob storage and command lines include "comp=metadata", indicating metadata operations, which can be used for malware C2 channels. (Malware C2 Comms over Azure Blob Metadata)
New rules identify Rockwell Automation devices in the environment and detect potential evasion of Defender for Endpoint by monitoring when antivirus mode is set to 'Passive' and related registry modifications occur. (CVSS 9.8 Rockwell Automation Impacted by High-Severity log4net Vulnerability, defendnot detection)
Feedback
Your input helps us improve! If you spot any issues, mistakes, or omissions in this digest issue, or have suggestions for new data sources to include, we'd love to hear from you. Contact us at team@rulecheck.io - we value your feedback and are committed to improving this resource for the detection engineering community.
Disclaimer
The summaries in this brief are generated autonomously by the OpenAI LLM model based on the provided system and user prompts. While every effort is made to consolidate accurate and relevant insights, the model may occasionally misinterpret, misrepresent, or hallucinate information. Readers are strongly advised to verify all key points by consulting the original sources linked in the brief for complete context and accuracy.
Powered by
This digest is built with BlackStork.
Looking for a customized version of this newsletter? We'd be happy to help — contact us.