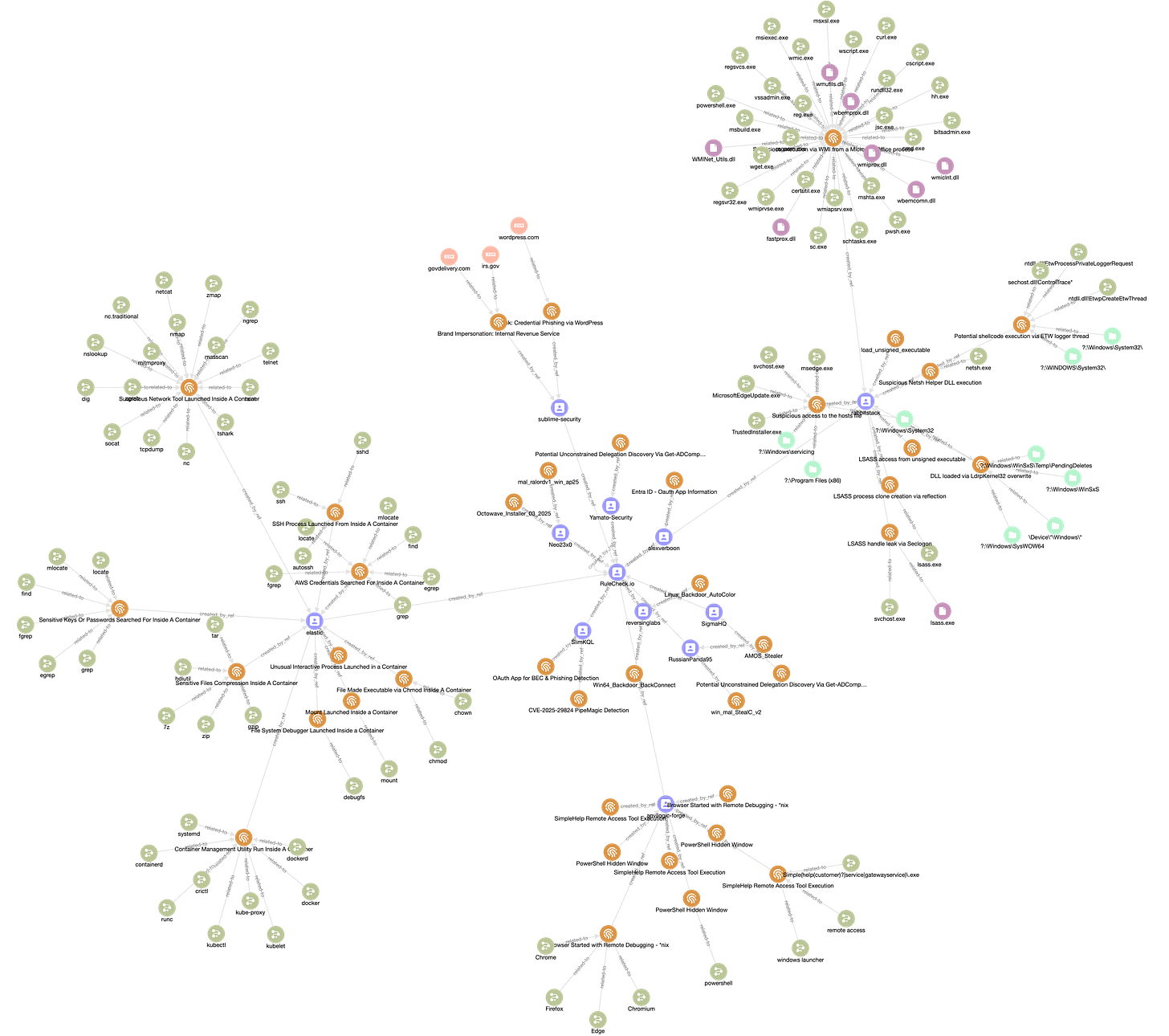
Detections Digest #20250414
The issue covers detection rule updates from 12 GitHub repositories between Apr 7 and Apr 14, 2025, including 40 new and 70 modified rules.
This week's update highlights the most significant changes to detection rules from 12 of the 40+ monitored GitHub repositories. Between Apr 7 and Apr 14, 2025, contributors added 40 new rules and updated 70 existing ones.
Stay informed on the latest changes in detection engineering to improve your threat detection coverage and operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Container security focus — Various new rules were introduced to monitor activities inside containers, such as privileged command use, unauthorized interactive processes, and network tool executions (elastic/detection-rules).
Expanding network data filtering — Several updates, especially for CVE-2023-23397 and subnet activities, focus on improved filtering and broader IPv6 support. These help improve detection of malicious activities in evolving network landscapes. (SigmaHQ/sigma, elastic/detection-rules)
YARA rule expansion for malware detection — Multiple repositories added YARA rules for identifying specific malware patterns, such as StealC, AMOS Stealer, and RALord Ransomware, which signifies a push towards targeting known malware signatures for better threat intelligence (RussianPanda95/Yara-Rules, Neo23x0/signature-base).
Use of AI tools for rule documentation — Incorporating generative AI in creating detailed triage and investigation guides for existing rules highlights a move towards operationalizing AI improvements in rule management processes (elastic/detection-rules).
Detection coverage for phishing and impersonation — New and updated rules focus on detecting brand impersonation, phishing messages, and service abuses (like Dropbox and DocuSign), especially integrating new beta features for profiling reply-to addresses (sublime-security/sublime-rules).
Improvements in cloud and key management — Updates to rules like AWS IAM key exposure and Snowflake data transfers emphasize better cloud environment security and management of access credentials, hinting at improving defenses in cloud infrastructure. (panther-labs/panther-analysis, elastic/detection-rules)
Wider use of Sysmon and telemetry data — Many rules, particularly for remote access tools and system process creations, leverage Sysmon logs and advanced telemetry data to strengthen endings of different evasion techniques and unauthorized access methods. (anvilogic-forge/armory, SigmaHQ/sigma)
Table Of Contents
SigmaHQ/sigma (+1, ✎9)
elastic/detection-rules (+10, ✎6)
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules (+1, ✎8)
sublime-security/sublime-rules (+2, ✎32)
🔔 Preview the STIX2 pack with all new detection rules and download it from GitHub:
Corporate repositories (7)
anvilogic-forge/armory (+8)
https://github.com/anvilogic-forge/armory
+ New rules
Two new detection rules were introduced to identify when browsers on Linux and Unix systems start with remote debugging flags. These rules target the possible abuse of debugging features, utilizing EDR logs and Splunk logic for identification. (Browser Started with Remote Debugging - *nix, Browser Started with Remote Debugging - *nix)
Three new detection rules focus on identifying PowerShell executions with hidden window commands. These rules aim to catch evasion techniques by threat actors and use different telemetry sources, including Splunk EDR and Winevent. (PowerShell Hidden Window, PowerShell Hidden Window, PowerShell Hidden Window)
Three new rules target the detection of SimpleHelp Remote Access Tool executions. These rules use different logging data, such as Winevent, Sysmon, and EDR, to monitor process creation events and file paths, aiming to identify potential unauthorized remote access activities. (SimpleHelp Remote Access Tool Execution, SimpleHelp Remote Access Tool Execution, SimpleHelp Remote Access Tool Execution)
SigmaHQ/sigma (+1, ✎9)
https://github.com/SigmaHQ/sigma
+ New rules
A new Sigma rule detects the use of the "Get-ADComputer" cmdlet to identify systems set for unconstrained delegation. This uses ScriptBlock logging conditions, aiding in tracing PowerShell activities that could indicate discovery operations on AD systems, (Potential Unconstrained Delegation Discovery Via Get-ADComputer - ScriptBlock).
✎ Modified rules
Detection for elevated system shells on Windows now includes monitoring for 'powershell_ise.exe', improving coverage against potential threats. This change is reflected in two rules aimed at improved tracking of shell and uncommon parent process activity (Elevated System Shell Spawned, Elevated System Shell Spawned From Uncommon Parent Location).
The rule tracking potential script or binary drops via PowerShell was updated by refining the directory filters, which better identifies unusual PowerShell actions (Potential Binary Or Script Dropper Via PowerShell).
Multiple rules saw changes targeting false positive reduction and accuracy improvements. Conhost process monitoring added exclusions for benign system service calls, WinAPI access detection improved by clarifying legitimate use cases, and Python network connections became more specific (Conhost Spawned By Uncommon Parent Process, Potential WinAPI Calls Via CommandLine, Python Initiated Connection).
The rule for CVE-2023-23397 exploitation now uses improved IPv6 filters and extended contains logic, adding detail and precision to network traffic analysis. An additional update introduced specific startswith checks for the Address field, fine-tuning detection for EventID 30804 over diverse IP patterns (Potential CVE-2023-23397 Exploitation Attempt - SMB).
A Linux buffer overflow detection rule witnessed a shift from stable to test status while undergoing regex pattern improvements and simplification to enhance detection performance (Buffer Overflow Attempts).
panther-labs/panther-analysis (✎3)
https://github.com/panther-labs/panther-analysis
✎ Modified rules
Changes to the Snowflake rules include simplifying detection logic by removing certain exclusion configurations and redundant functions in the snowflake_stream_external_shares.py. The “Snowflake External Data Share” rule got a streamlined testing process by removing unnecessary tags and redundant fields, focusing tests on critical elements (snowflake_stream_external_shares, Snowflake External Data Share).
The AWS rule for detecting compromised keys has been updated to include new policies, broadening its detection scope. The update now covers additional scenarios involving key exposure and quarantine with the inclusion of 'AWSCompromisedKeyQuarantineV2' and 'AWSCompromisedKeyQuarantineV3' policies, improving the rule's effectiveness (aws_key_compromised).
Cybersec Feeds Overview newsletter consolidates updates from 80+ sources: government organizations, cybersecurity vendors, threat intelligence teams, security research labs, and blogs from cybersecurity communities and professionals.
elastic/detection-rules (+10, ✎6)
https://github.com/elastic/detection-rules
+ New rules
New rules focus on detecting various suspicious activities within Linux containers. These include privilege escalation attempts via DebugFS, mounting, and altering file permissions using chmod or chown, and execution of suspicious network and management tools. Container activity monitored includes unexpected interactive processes, unusual network tool usage, and execution of container management utilities, aiming to improve detection of security threats (File System Debugger Launched Inside a Container, Mount Launched Inside a Container, File Made Executable via Chmod Inside A Container, Suspicious Network Tool Launched Inside A Container, Container Management Utility Run Inside A Container, Unusual Interactive Process Launched in a Container).
Other rules target unauthorized credential access by identifying suspicious activities involving AWS credentials, sensitive keys, passwords, and compression of sensitive files within containers. The detection logic includes monitoring of search utilities for sensitive file access, improving the ability to detect potential unauthorized actions and data exfiltration attempts within containerized environments (AWS Credentials Searched For Inside A Container, Sensitive Keys Or Passwords Searched For Inside A Container, Sensitive Files Compression Inside A Container).
A specific rule is introduced for detecting SSH and related process executions within containers, mapped to Lateral Movement and Persistence tactics. This aims to strengthen security posture by monitoring SSH, SSHD, and autossh processes that might signal lateral movement actions (SSH Process Launched From Inside A Container).
✎ Modified rules
The rule "Shared Object Created or Changed by Previously Unknown Process" for Linux was improved by expanding query logic to cover more file extension, name patterns, and paths. Process name exclusions were refined to improve unauthorized modification detection while reducing false positives. (Shared Object Created or Changed by Previously Unknown Process)
For the rule "Suspicious Execution via Scheduled Task" on Windows, new exceptions were added for benign PowerShell scripts executed by the system account. This refines detection by excluding false positives from known scripts in specific paths. (Suspicious Execution via Scheduled Task)
Several Linux rules were improved by including 'host.name' in the query logic. These changes improve the context and precision for identifying hosts involved in scanning, file transfers, brute-force attempts, and command executions. (Potential Subnet Scanning Activity from Compromised Host, Unusual File Transfer Utility Launched, Potential Malware-Driven SSH Brute Force Attempt, Unusual Command Execution from Web Server Parent)
reversinglabs/reversinglabs-yara-rules (+2)
https://github.com/reversinglabs/reversinglabs-yara-rules/
+ New rules
Two new YARA rules have been introduced to detect specific backdoor malware. The "Win64_Backdoor_BackConnect" rule identifies the BackConnect backdoor on Win64 systems by monitoring network communication and system calls. Meanwhile, the "Linux_Backdoor_AutoColor" rule targets the AutoColor backdoor on Linux systems by tracking execution patterns characteristic of this malware, which helps improve detection coverage across different operating systems. (Win64_Backdoor_BackConnect, Linux_Backdoor_AutoColor)
Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules (+1, ✎8)
https://github.com/Yamato-Security/hayabusa-rules
+ New rules
Added a new Sigma rule for identifying systems with unconstrained delegation configurations using the Get-ADComputer cmdlet via Windows Script Block Logging, which aids in spotting potential misuse of AD computer delegation settings (Potential Unconstrained Delegation Discovery Via Get-ADComputer - ScriptBlock).
✎ Modified rules
Multiple rules were refined to improve accuracy and reduce false positives. Filters were added or adjusted in "Potential WinAPI Calls Via CommandLine" for better exclusion of benign processes and to provide clearer guidance on false positives. The "Elevated System Shell Spawned From Uncommon Parent Location" rule added identifiers for PowerShell and refined conditions for parent processes to improve path detection without producing false alerts (Potential WinAPI Calls Via CommandLine, Potential WinAPI Calls Via CommandLine, Elevated System Shell Spawned From Uncommon Parent Location).
The "Potential CVE-2023-23397 Exploitation Attempt - SMB" rule was updated with additional CIDR and IPv6 socket filters, refining IP address specificity needed to effectively detect these exploitation attempts (Potential CVE-2023-23397 Exploitation Attempt - SMB).
The "Potential Binary Or Script Dropper Via PowerShell" rule now includes additional temporary directories like 'C:\Windows\SystemTemp' to accurately detect potential dropper activities, thus refining assumptions for detected binaries (Potential Binary Or Script Dropper Via PowerShell).
The "Python Initiated Connection" rule incorporated a '.exe' inclusion to refine the application filter, thus ensuring accurate detections of process initiators (Python Initiated Connection).
Changes to the "Whoami.EXE Execution Anomaly" and "Elevated System Shell Spawned" rules involved extending the selection criteria to incorporate additional parent process scenarios, reducing false negatives, and broadening real-time detection coverage (Whoami.EXE Execution Anomaly, Elevated System Shell Spawned).
sublime-security/sublime-rules (+2, ✎32)
https://github.com/sublime-security/sublime-rules
+ New rules
Two new detection rules have been added: one to identify credential phishing attempts via non-WordPress senders linking to suspicious WordPress sites by analyzing email links, and another to detect brand impersonation of the Internal Revenue Service using sender display name and content indicators, excluding legitimate IRS domains (Link: Credential Phishing via WordPress, Brand Impersonation: Internal Revenue Service).
✎ Modified rules
Rules were modified to utilize beta features for profiling reply-to addresses across various service abuse scenarios, including DocSend, DocuSign, Dropbox, QuickBooks, Google Drive, SharePoint, and suspicious reply-to domains. These updates simplify the logic, replace deprecated checks, and refine conditions to reduce false positives and improve detection accuracy for unsolicited emails and service abuse, potentially at the cost of stability due to the features' beta status. (DocSend Share From an Unsolicited Reply-To Address, DocuSign Share From an Unsolicited Reply-To Address, Dropbox Share From New Domain, Dropbox Share From an Unsolicited Reply-To Address, QuickBooks Notification From New Domain, Google Drive Share From an Unsolicited Reply-To Address, Link: Secure SharePoint file share from new or unusual sender, Suspicious DocuSign Share From New Domain, Suspicious newly registered reply-to domain with engaging financial or urgent language, Suspicious SharePoint File Sharing, Service Abuse: DocuSign Notification with Suspicious Sender or Document Name)
Several rules were amended to improve phishing detection involving Microsoft Forms, Google Drive, DocuSign, and SharePoint by updating logic for identifying phishing forms, abnormal spacing, new display name matching, and engaging language usage. They now include conditions to reduce false positives and improve validation of phishing indicators like URL shortcuts, sender email solicitation errors, and specific HR language usage. (Link: Multistage Landing - Microsoft Forms Abuse, Credential Phishing: Fake Storage alerts (unsolicited), Link: Multistage Landing - Abused Docusign, Link: Multistage Landing - Abused Google Drive, Credential phishing: Engaging language and other indicators (untrusted sender), Corporate Services Impersonation Phishing)
Rules like DocuSign, SharePoint, and voicemail notifications were refined with additional checks and criteria adjustments, such as attachment count thresholds, exclusion of known benign message types, and expanding detection to include known trusted domains like 'google.com'. These changes aim to prevent both false positives and false negatives by cross-verifying conditions more intensely against established baselines. (Attachment: Fake attachment image lure, Fake voicemail notification (untrusted sender), Credential Phishing: Suspicious E-sign Agreement Document Notification)
Brand impersonation detection rules were refined with regex adjustments, logic simplifications, and inclusivity checks for sender profiles to heighten coverage for brands like Booking.com, Microsoft, UPS, Meta, and Google notifications. This update specifically targets linguistic manipulations and how sender names are presented, aiming to plug gaps used by phishing scams. (Brand Impersonation: Booking.com, Brand impersonation: Microsoft with low reputation links, Brand impersonation: UPS, Brand Impersonation: Meta and Subsidiaries, Google Share Notification with Suspicious Comments)
Adjustments to rules related to email scams and phishing like Advance Fee Fraud and Piano Giveaway scams involved regex pattern expansions and thematic filtering, focusing on email bodies and attachments. This updates the ability to discern legitimate messages from malicious attempts by integrating machine learning-driven topic analysis. (Advance Fee Fraud (AFF) from freemail provider or suspicious TLD, Scam: Piano Giveaway, Attachment: Adobe image lure in body or attachment with suspicious link)
Personal repositories (5)
RussianPanda95/Yara-Rules (+2)
https://github.com/RussianPanda95/Yara-Rules
+ New rules
Two new YARA rules have been introduced to detect malware. The "win_mal_StealC_v2" rule targets the StealC v2 malware by matching specific string and binary patterns, considering file size and content structure. The "AMOS_Stealer" rule identifies the AMOS Stealer malware by matching particular byte sequences and file headers. (win_mal_StealC_v2, AMOS_Stealer)
Neo23x0/signature-base (+2)
https://github.com/Neo23x0/signature-base
+ New rules
Two new YARA rules were introduced for malware detection. The 'mal_ralordv1_win_ap25' rule identifies components of RALord Ransomware, utilizing specific string patterns with the 'wide' modifier, and sets the detection score at 100. Meanwhile, the 'Octowave_Installer_03_2025' rule targets resources in Octowave Loader MSI installers, based on hash values, strings, file size limits, and ASCII strings detection. This broadens detection capabilities for these threats (mal_ralordv1_win_ap25, Octowave_Installer_03_2025).
SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules (+2)
https://github.com/SlimKQL/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules
+ New rules
A new KQL rule detects exploitation of the CLFS zero-day vulnerability CVE-2025-29824, which could lead to ransomware actions. The rule monitors suspicious named pipe events (CVE-2025-29824 PipeMagic Detection).
Another new rule targets rogue OAuth applications to detect potential BEC and phishing activities. It identifies unverified apps from external sources with sensitive permissions, added within the last hour (OAuth App for BEC & Phishing Detection).
rabbitstack/fibratus (+9, ✎3)
https://github.com/rabbitstack/fibratus
+ New rules
New detection rules were introduced to monitor unauthorized access and potential threats against LSASS. These include detecting access from unsigned executables, process clone creation via reflection, and handle leaks via Seclogon, which reveal potential credential dumping activities (LSASS access from unsigned executable, LSASS process clone creation via reflection, LSASS handle leak via Seclogon).
Multiple rules improve Defense Evasion detection by focusing on suspicious DLL loading tactics and process injection methods. New rules detect malicious DLL loading via LdrpKernel32 overwrite, potential shellcode execution via the ETW logger thread, and suspicious access to the hosts file, all targeting common evasion methods (DLL loaded via LdrpKernel32 overwrite, Potential shellcode execution via ETW logger thread, Suspicious access to the hosts file).
A new rule tracks suspicious activities that might indicate Initial Access attempts through the use of WMI by Microsoft Office processes, focusing on unusual DLL loads and subsequent process spawns (Suspicious execution via WMI from a Microsoft Office process).
A new rule for Persistence detection identifies the use of the Netsh Helper DLL for potential adversary installation attempts. It checks for sequences that spawn netsh.exe leading to create_thread events involving insecure modules (Suspicious Netsh Helper DLL execution).
A macro named 'load_unsigned_executable' was added to help detect when unsigned executables load based on the image signature type, assisting in tracking potentially malicious process initiations (load_unsigned_executable).
✎ Modified rules
The "Unsigned DLL injection via remote thread" rule was improved by including thread start address symbol matching for functions, fixing the 'svchost.exe' path pattern with a wildcard drive letter, and applying exact quotation for 'ngen.exe'. (Unsigned DLL injection via remote thread)
The rule for "Script interpreter host or untrusted process persistence" was improved by adding an exclusion for PID 4 and broadening the exclusion list to include processes like GoogleDriveFS and Dropbox. It now monitors if script interpreters or untrusted executables modify registry run keys or create files in startup locations, with attention to signed and trusted executables. (Script interpreter host or untrusted process persistence)
The "Potential privilege escalation via phantom DLL hijacking" rule was updated to reduce false positives by excluding certain benign processes like 'svchost.exe' and adding a condition to ignore system process (PID 4). (Potential privilege escalation via phantom DLL hijacking)
alexverboon/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules (+1)
https://github.com/alexverboon/Hunting-Queries-Detection-Rules
+ New rules
A new rule was added to query the OAuthAppInfo table in Defender XDR, which provides a summary of application permission levels and related metadata for detailed analysis (Entra ID - Oauth App Information).
Feedback
Your input helps us improve! If you spot any issues, mistakes, or omissions in this digest issue, or have suggestions for new data sources to include, we'd love to hear from you. Contact us at team@rulecheck.io - we value your feedback and are committed to improving this resource for the detection engineering community.
Disclaimer
The summaries in this brief are generated autonomously by the OpenAI LLM model based on the provided system and user prompts. While every effort is made to consolidate accurate and relevant insights, the model may occasionally misinterpret, misrepresent, or hallucinate information. Readers are strongly advised to verify all key points by consulting the original sources linked in the brief for complete context and accuracy.
Powered by
This digest is made possible through our partnership with BlackStork, combining their content generation technology with our detection engineering expertise to deliver timely, high-quality updates straight to your inbox.
Looking for a customized version of this newsletter? We'd be happy to help — contact us.